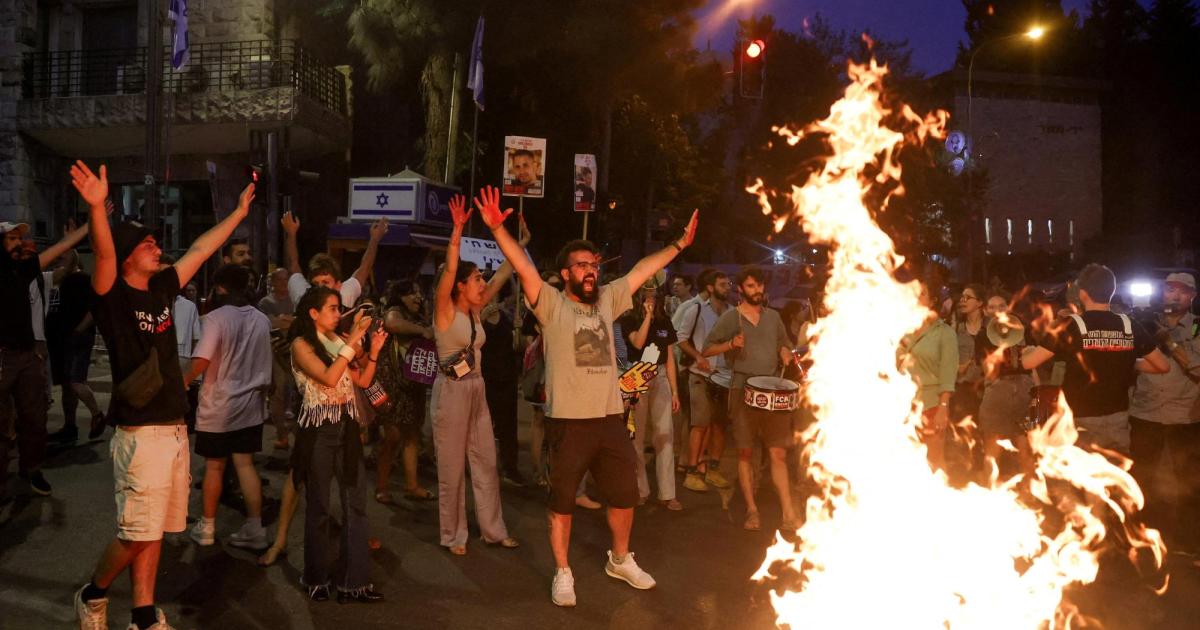A new training center in Brandon is set to tackle the shortage of healthcare...
AMC Theatres has appointed Stephanie Tierney as Vice President of Distribution. This new role...
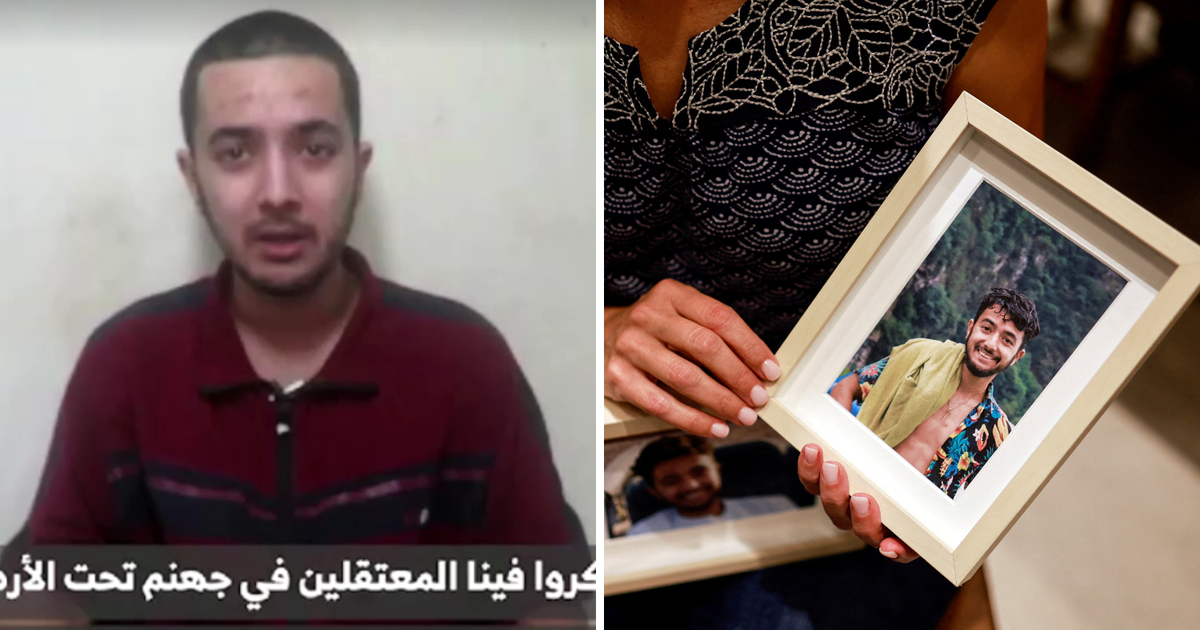
Hersh Goldberg-Polin, an Israeli with an American passport, was abducted on October 7th at...
In the first quarter of 2024, Align Technology, Inc. reported strong financial results that...
The United States has agreed with Israel’s dissatisfaction with reports of mass graves in...
The US Congress is considering forcing a change of ownership of the popular video...
The Syktyvkar city court has issued an arrest warrant in absentia for world chess...
A New Jersey Superior Court Appellate Division ruling has opened the door for relatives...
The Independent Fiscal Responsibility Authority (AIReF) has unveiled a new tool to analyze the...
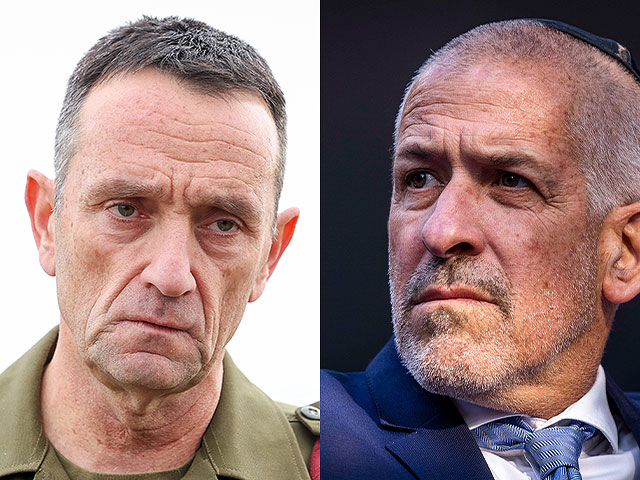
On April 24, Israeli Chief of Staff Herzi A-Levi and the head of the...