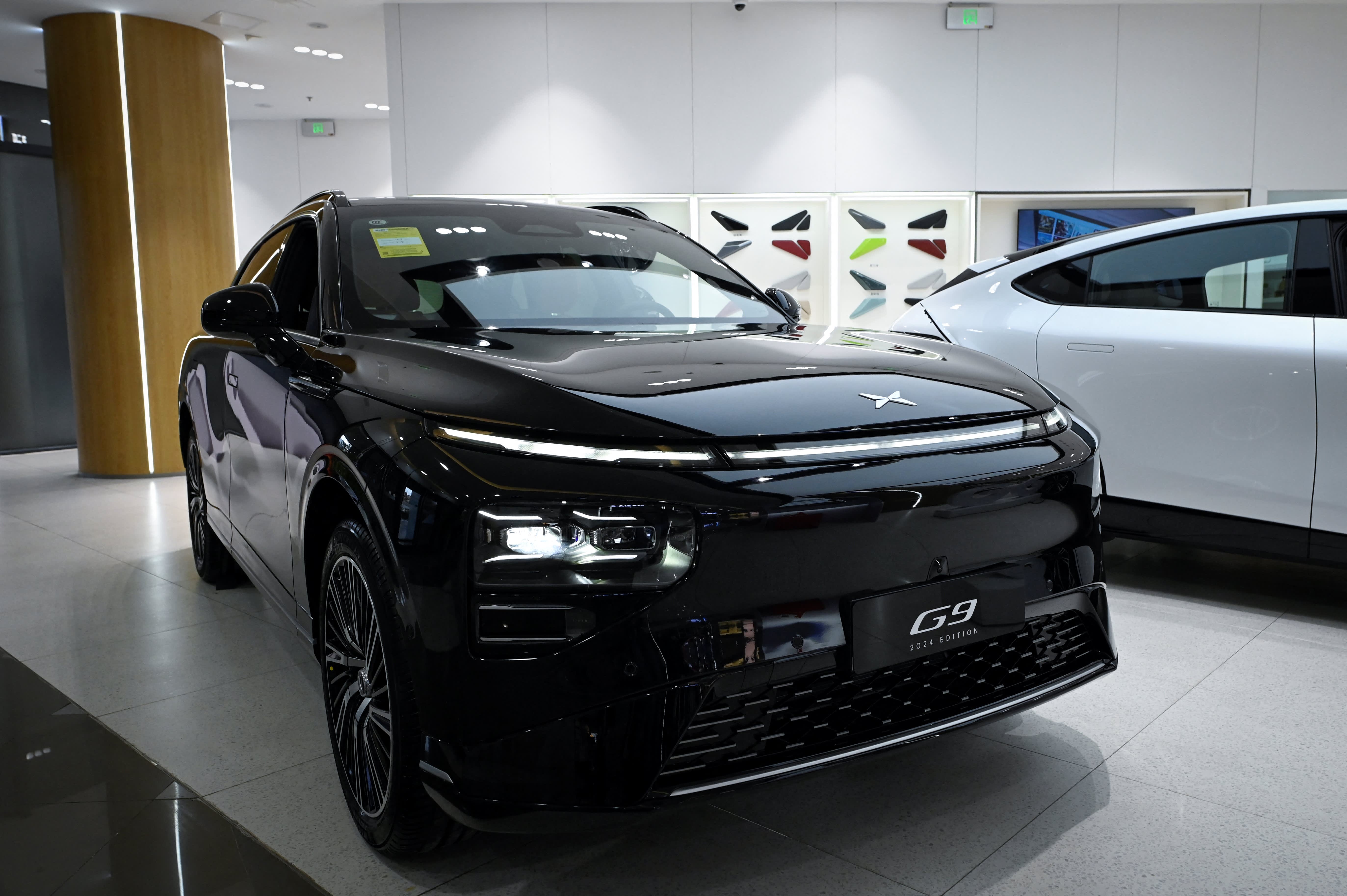
The Xpeng G9 has recently caught the attention of many onlookers at a mall...
On Saturday, New Ulm baseball was victorious against Worthington. Luke Suess played a pivotal...
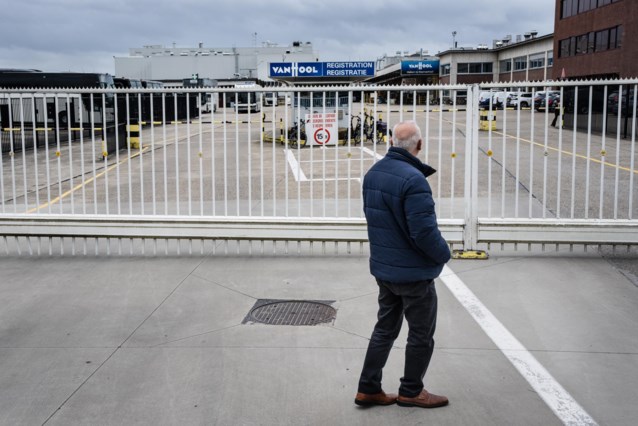
The first group of employees at Van Hool’s trailer division is expected to return...
On April 19, 2024, a pilot study published in the Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine...
A recent study by ACCA and IMA reveals that finance professionals are feeling optimistic...
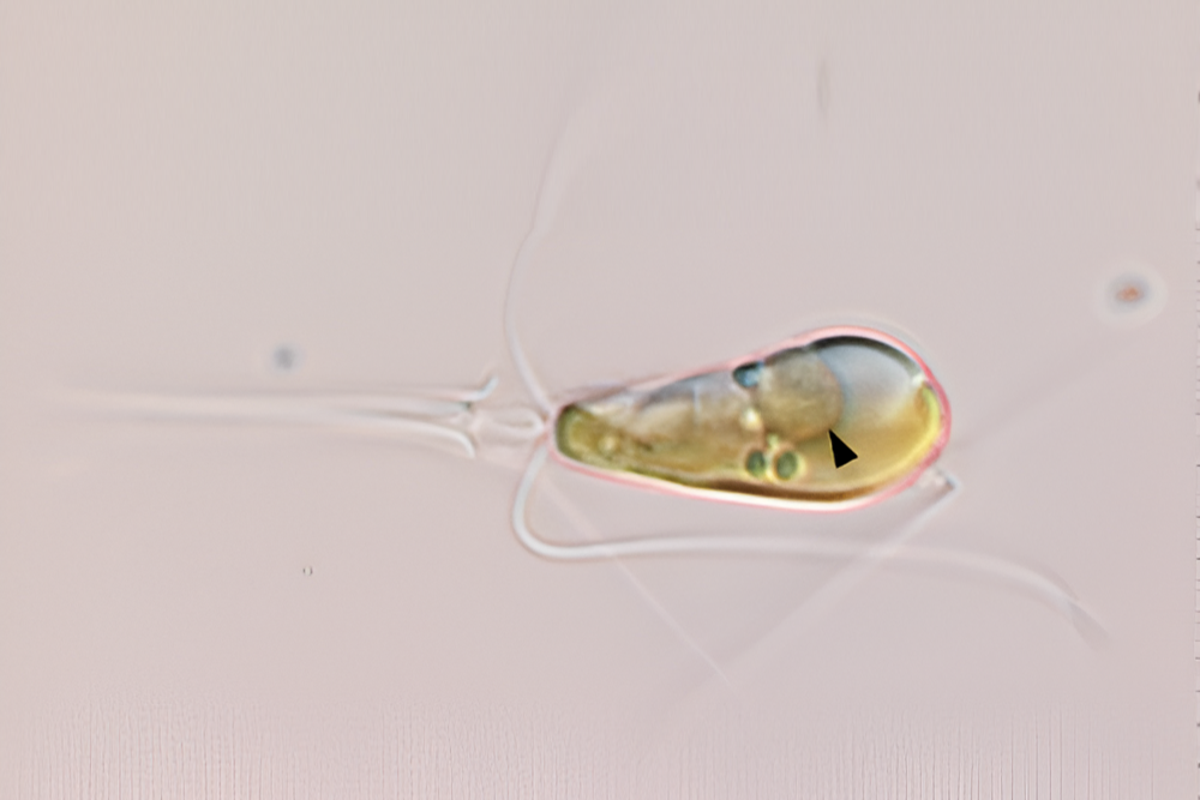
In a groundbreaking evolutionary event, two lifeforms have merged to form a single organism...
German politicians and business leaders are increasingly discussing a topic that was previously considered...
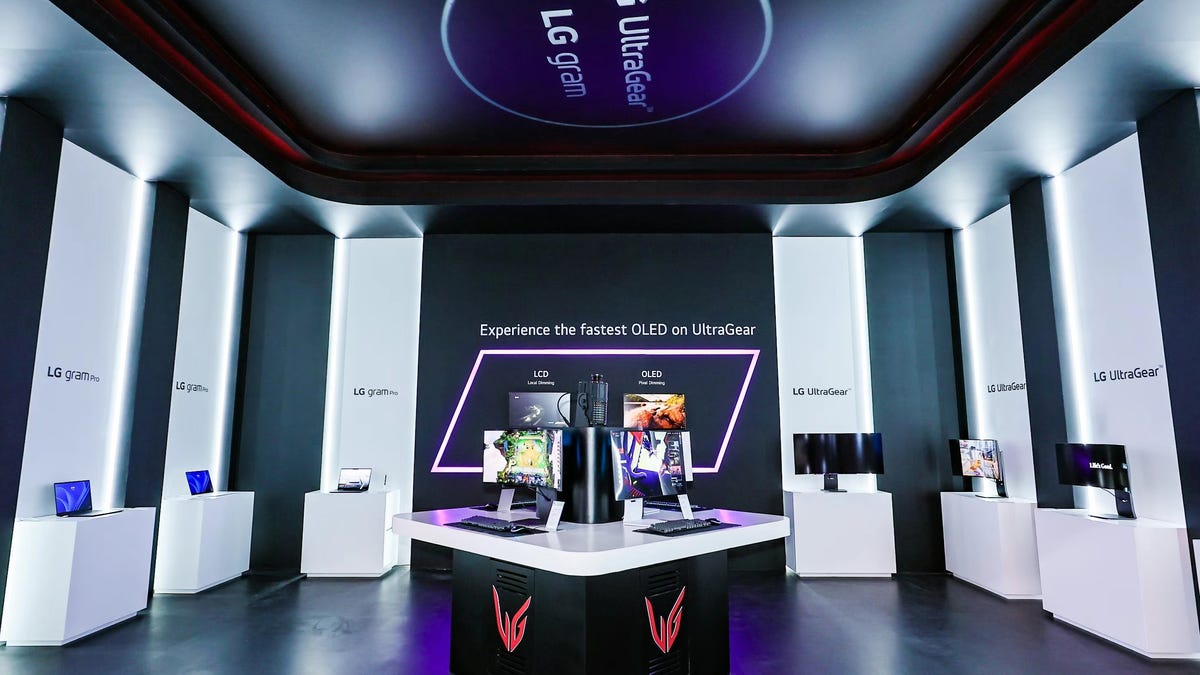
In the first quarter, LG Electronics’ TV business returned to profitability thanks to the...
In Miami Township, the use of drones has been a game changer in enhancing...
Licking Heights Local Schools has received an investment from the Governor’s Office of Workforce...